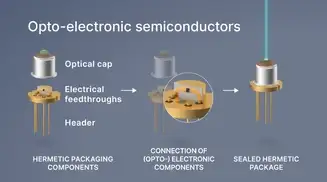
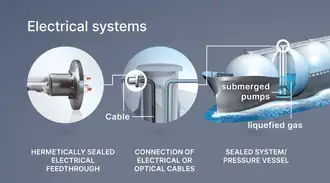
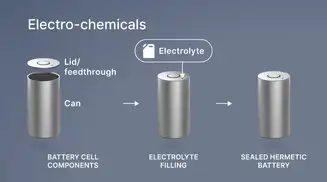
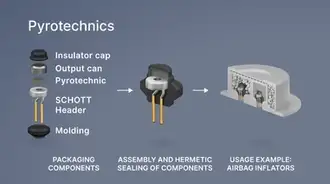
Hermetic packaging
What is hermetic packaging? What is hermetic sealing?
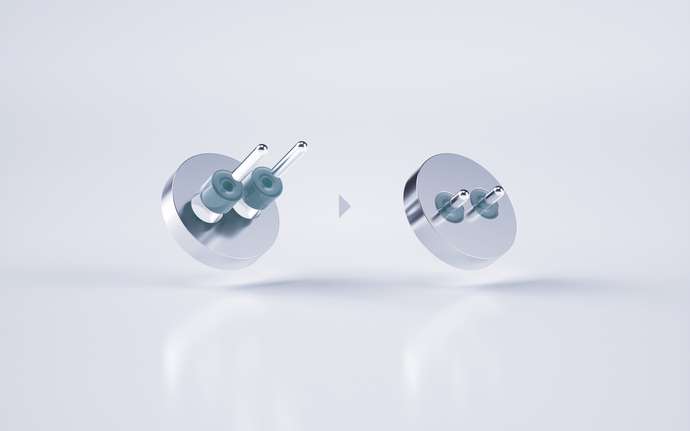
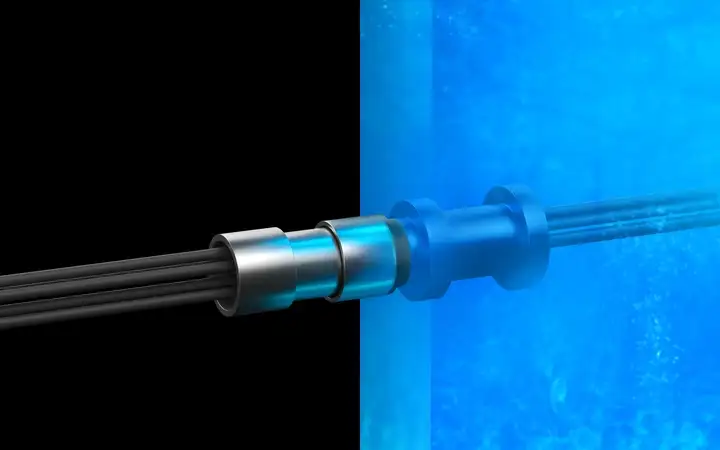
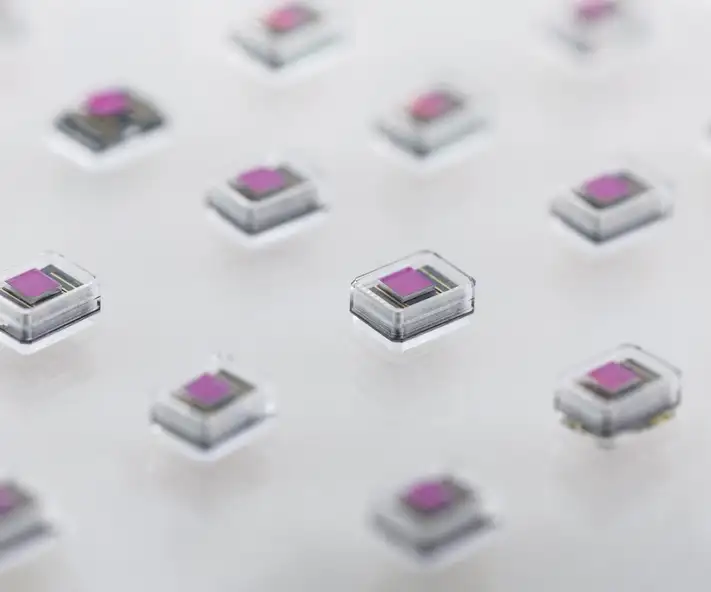
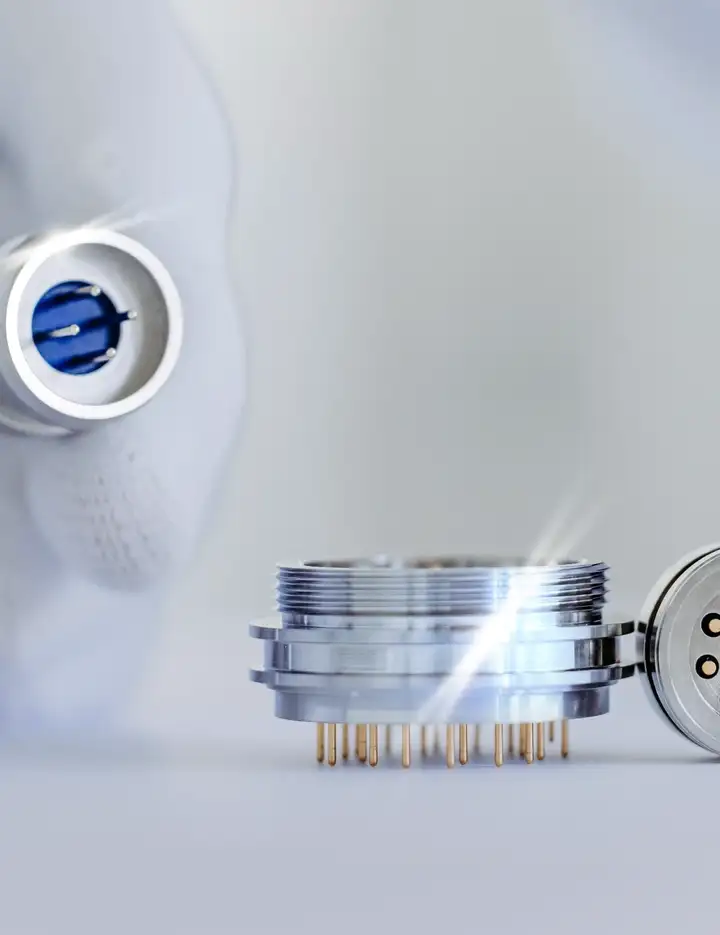
Hermetic packaging, or sealing, is primarily used in electronic packaging to protect sensitive components like electrical parts, optoelectronic chips, and semiconductors in vacuum-tight housings. It can also safeguard entire electrical assemblies and systems or encapsulate electrochemical and pyrotechnic materials. The key function is to block moisture, dust, and contaminants while allowing electrical power or optical signals to pass through.Hermetic packaging refers to both the process and the component formats used. Hermetic sealing, on the other hand, can also refer to the materials such as sealing glasses or metal solders used to create a gas-tight bond.
What are the benefits of hermetic packaging?
Hermetic packages, feedthroughs, headers, and connectors are commonly used to safeguard sensitive electronics and materials in demanding environments, ensuring reliability and safety. They also foster innovation by providing enhanced performance and efficiency for many applications.Reliable moisture barrier
Hermetic seals provide the highest level of protection against the ingress of moisture, as well as gases, and contaminants. By creating an airtight enclosure, they can prevent dew formation inside the cavity, which could otherwise lead to short circuits, corrosion, and damage. Only a truly vacuum-tight barrier, combined with a stable internal atmosphere, can effectively prevent dew from forming.
Robustness in harsh operating conditions
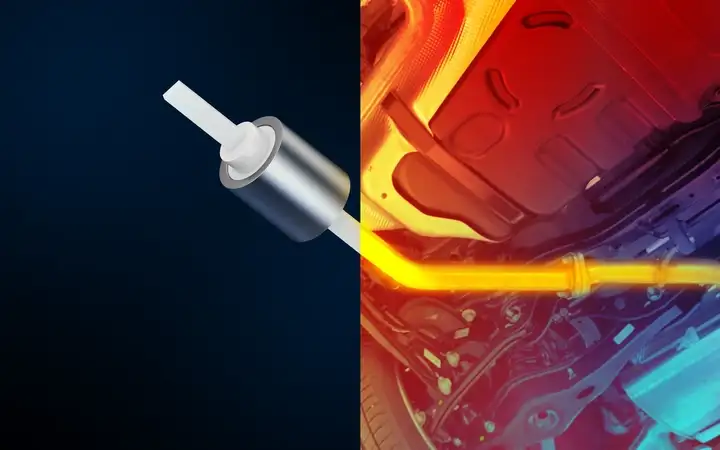
Hermeticity is often essential in applications with high temperatures, high pressures, or harsh chemical environments, where non-hermetic seals using organic materials would fail.
Long-term reliability and safety
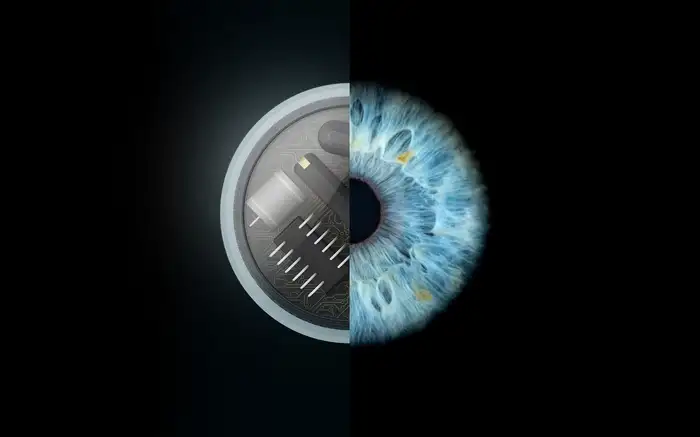
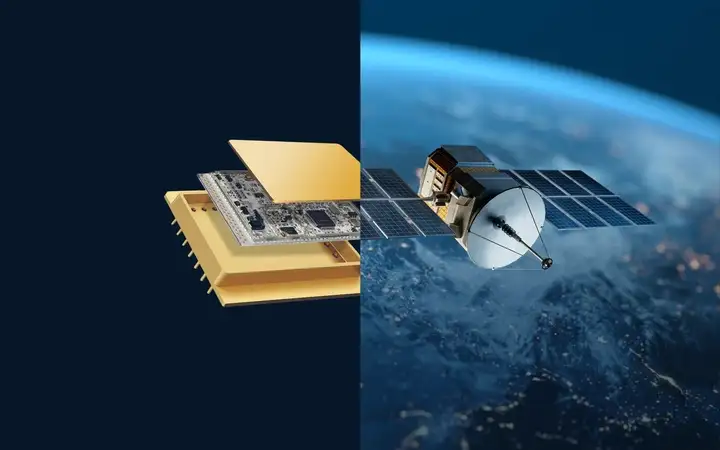
Gas-tight packages enable longevity and safety of components, particularly in critical environments where accessibility for repair or replacement is limited, such as medical implants or aerospace application.
Improved design and cost-efficiency
Innovative hermetically sealed designs can be smaller, lighter, easier to process, and offer better cost-of-ownership than non-hermetic alternatives.
Enhanced performance
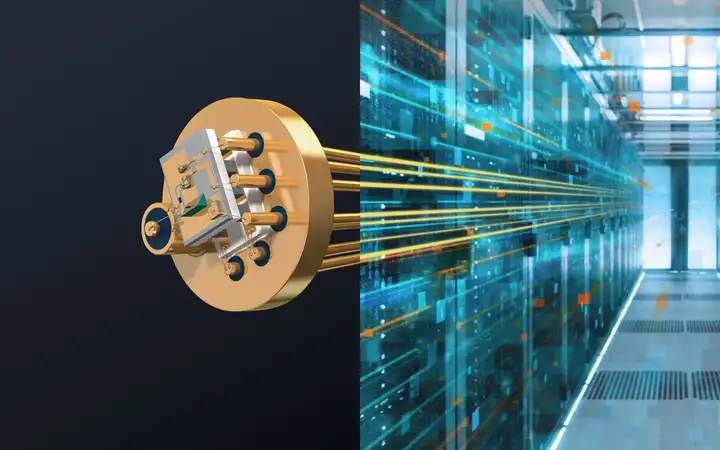
Hermeticity can be the key factor in enhancing the performance of enclosed components, assemblies, or systems, particularly for applications related to high-speed or high-frequency signal transmission.
Dive into a video series with neurotechnology expert Claude Clément as he explains hermetic packaging
Application examples of hermetic packaging
Explore typical application examples across diverse markets and industries, from automotive and aerospace to batteries, consumer electronics, energy, industrial automation, medical devices, optoelectronics, and security and defenseWhat is the difference between hermetic and non-hermetic packaging?
Although the term hermetic is often confused with airtight, it refers to a durable, gas-tight seal that lasts even in tough conditions. Only enclosures and seals made using inorganic materials like glass, metal, and ceramics can provide true hermeticity because they have near-zero permeation.On the other hand, organic polymers and epoxies are inherently non-hermetic. Although commonly used for certain types of electronic packaging, they will allow moisture to penetrate over time. This can lead to reliability issues or even system failure.
Selecting a hermetic or non-hermetic solution depends on the sensitivity of the enclosed components, safety, performance and durability requirements, and the operating conditions.
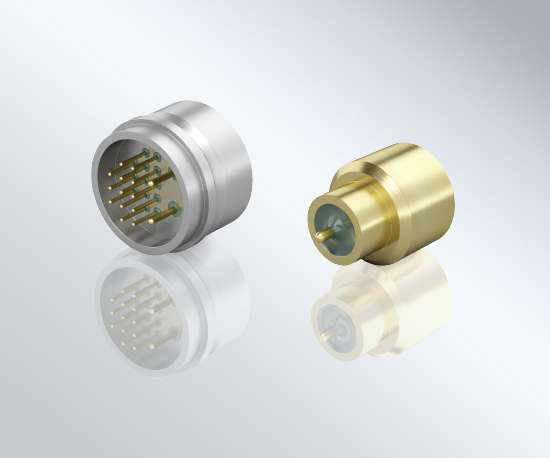
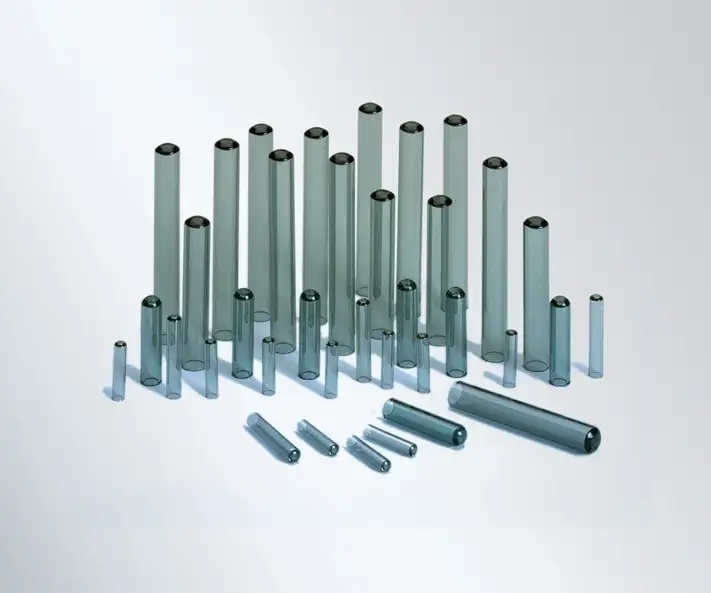
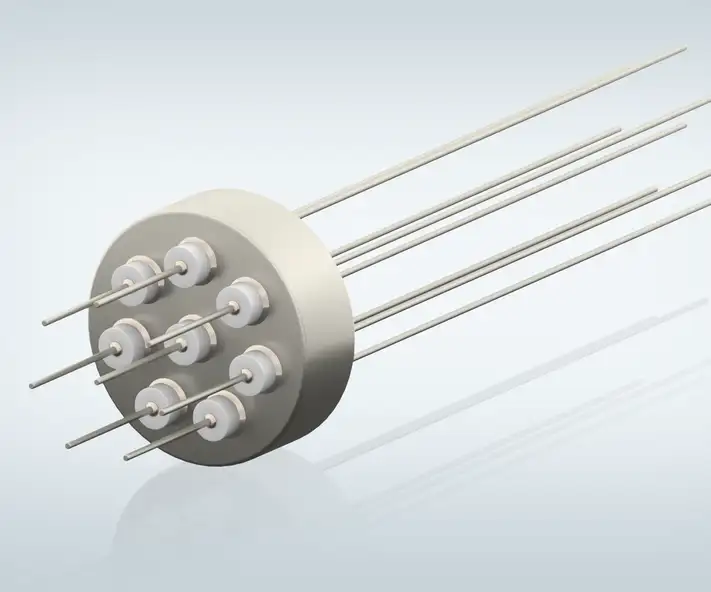
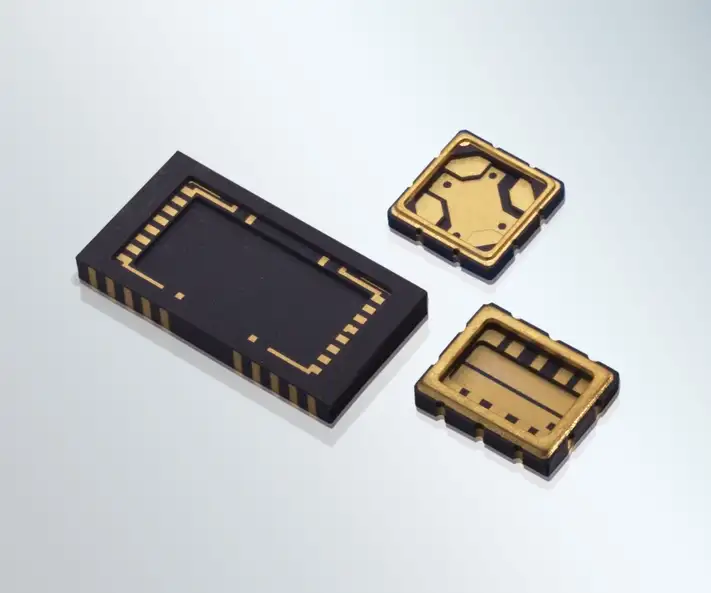
What types of hermetic packaging are available?
While some terms are used interchangeably, here is a brief overview of common hermetic packaging formats and typical terminology.




SCHOTT know-how
With a 140-year heritage in specialty glass and 80 years in hermetic sealing, SCHOTT is a unique partner for reliable packaging solutions.As a global technology group, customers trust our dependable, problem-solving expertise and innovative manufacturing technologies. Whether you need standard or custom solutions, we consistently deliver exceptional quality and value across industries. Explore SCHOTT’s technology and product portfolio via the links below or contact us for more information.
Want to know more? Let's talk
Whether you need more information or advice for a project, I would be delighted to talk to you.